Hydronic Central Heating Systems
On this page you will find sections on:
- Types of Heating Systems?
- What is Hydronic Central Heating?
- What is A Fully Pumped Central Heating System?
- If I Don't Like Radiators, Can I Still Have Central Heating?
- Must I Store Hot Water?
- What Benefits Do I Get With A Combination Boiler?
- What Else Should I Know?
- What is A Condensing Boiler?
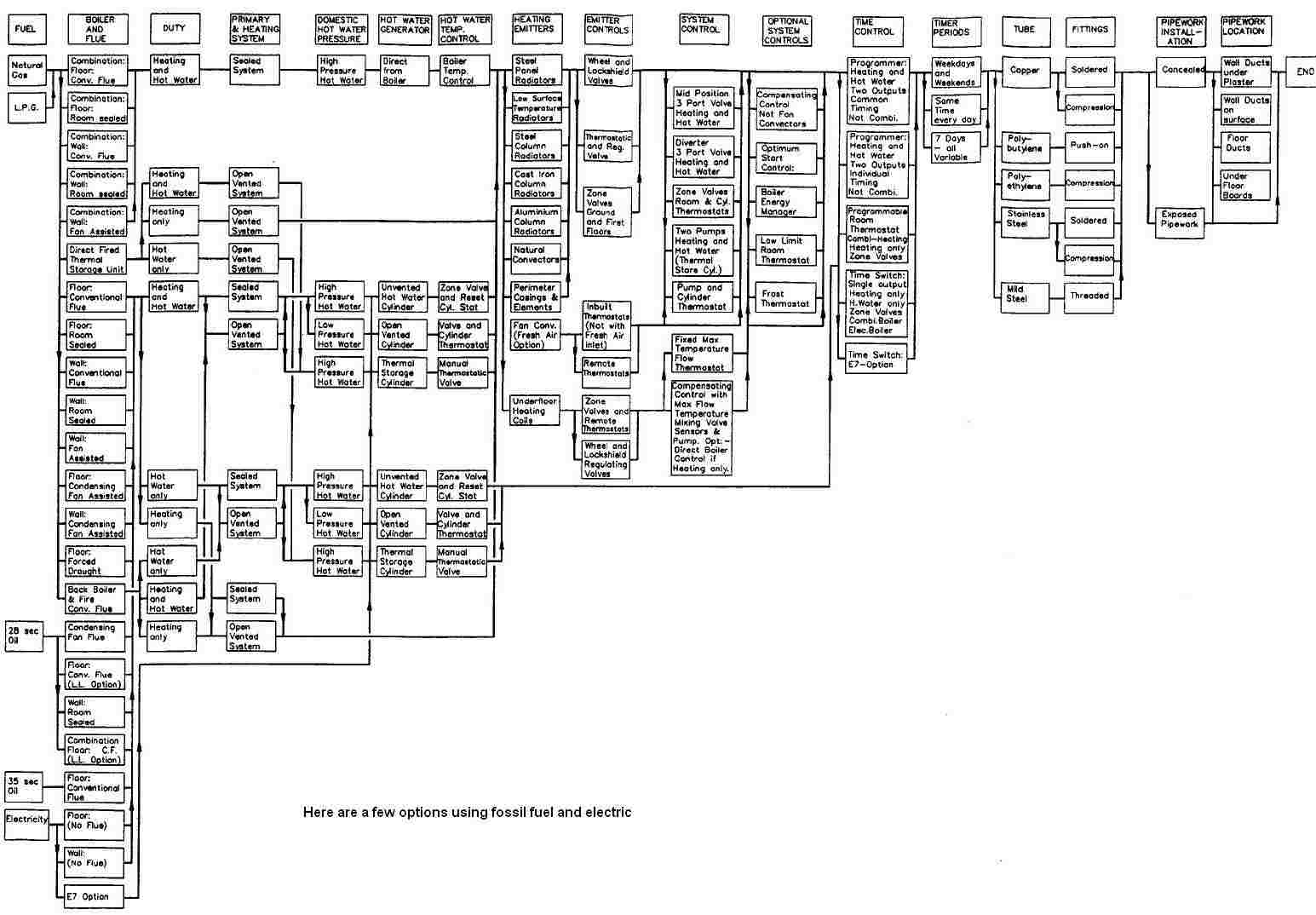
- Types of Domestic Hydronic Central Heating Systems
- More information and Links

To view any thumbnail simply click on the image to enlarge
Types of Heating Systems?
There are four categories that space heating systems generally fall into;
- Wet - water based (hydronic systems)
- Dry - warm/forced air systems
- Radiant - underfloor heating
- Electric storage - heated at cheaper night rate for slow day release generally designed for localized space heating although central heating units are available. Electric radiant heaters are also localized heaters.
- In the UK economy 7 option means heating hot water for storage or storage heaters at night or off-peak rate.
You can install a combination of any of these into a building.
The central heating systems discussed on this page refers to hydronic central heating (water based) systems only.
What is Hydronic Central Heating?
open vented central heating and open vented hot water storage Hydronic central heating is the use of a heat generator commonly called a boiler (or furnace) to raise the temperature of a heating medium, generally water.
The heated water (sometimes referred to as hydronic systems or wet systems) is then circulated from the home heating boiler through pipes to heat emitters (radiators, convectors and underfloor heating coils), through which the water loses its heat to the room. The cooler water then returns to the boiler for reheating.
Central heating generally means that there is commonly only one heat source (the boiler) that provides both space heating and domestic hot water for the entire house.
You can system-link a number of boilers together in a hydronic central heating system depending on the systems required output for both space heating and hot water provision but most family sized homes only require one.
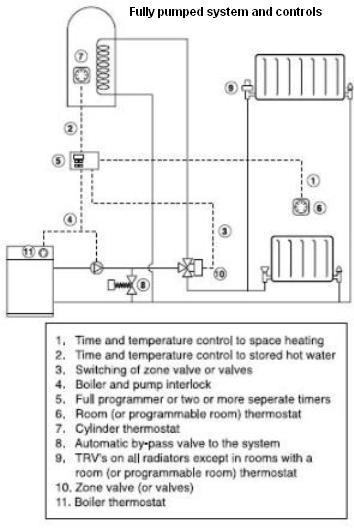
What is A Fully Pumped Central Heating System?
A fully pumped hydronic central heating system is one in which water from the boiler is circulated (not pumped as commonly referred) by a circulator to both the hot water radiators and through the heat exchanger (the coil) inside indirect hot water storage cylinders (hot water storage optional). This system incorporates a full range of control options.
Generally a fully pumped hydronic central heating system will have a circulator, a room thermostat, cylinder thermostat, a programmer for heating and hot water, a 3 port motorized valve, (or two 2 port motorized valves), and an automatic by-pass valve.
Note: Central heating can also be provided by ducted 'forced air' systems and multi-split air heat pumps systems.
For example, a multi-split system has multiple indoor units (a unit in each room) connected to a single outdoor unit - this system can have 2 to 8 indoor units connected to a single outdoor unit.
Many of today's brands of heat pumps have 'inverters'. This technology allows the system to match the compressor's speed output to your indoor heating or cooling load conditions.
Basically this means that a heat pump with inverter is a system that can slow down the speed of the fan and the compressor to maintain your ideal environment and in so doing offer greater energy savings over the fixed speed heat pumps that run at full speed then switch off when the thermostat is satisfied and then repeat the process when the temperature has fallen.
Most domestic air-conditioners and heat pumps are the same thing as they generally have a reverse cycle, summer cooling and winter heating.
There are some air heat pumps that can work in temperatures as low as -10 to -15°C, and the efficiency of this technology is continually improving.
Got any good plumbing tips? |
 |
For info on hot water heat pumps click here.
If I Don't Like Radiators, Can I Still Have Central Heating?
Yes, hydronic central heating systems are not restricted to just using radiators as the heat emitter. Central heating just means that there is one, or more than one boiler 'system-linked', as the 'central heating' generator for that building.

So your home heating boiler can provide heat to any suitable heat emitter, and that could be radiators, underfloor heating coils, skirting convector heaters/baseboards, fan assisted converter heaters, or a combination of all.
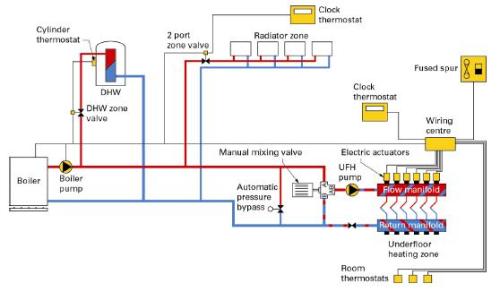
The picture above shows a typical schematic for a hydronic central heating system using a conventional boiler that provides heat for underfloor heating pipes (coils), radiators, and stored domestic hot water. You can also use a system boiler to provide heat and hot water.
A system boiler is basically a mains fed appliance, a high pressure system that now houses internally some of the components that were previously installed elsewhere in hydronic central heating systems but not inside the boiler itself.
For example the ciculator pump, diverter valve, by-pass valve, expansion vessel and filling loop are all now housed inside the boiler, hence the name 'system boiler'.
A conventional boiler or a system boiler can be used to provide just heat or just hot water or both.
Must I Store Hot Water?
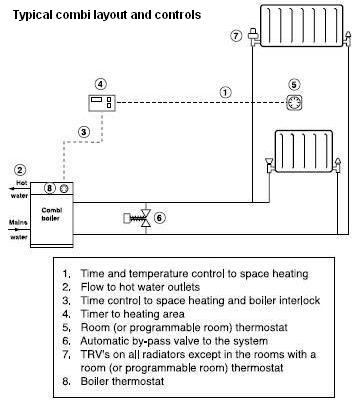
You don't have to have store hot water if you don't want to. If your home is small, or you don't have the space for storage, (for example a small flat or apartment), then you could use a 'combination boiler' which provides both hot water on demand and heating.
Hot water on demand is simply this - as soon as you turn on a hot tap/faucet the burner inside the boiler fires up and heats the water instantly.
If you are a single person, or one that is hardly at home, then a combination (Combi) boiler would be for you as there is no wasting of money and energy heating and storing water that you may not use.
What Benefits Do I Get With A Combination Boiler?
There are financial advantages with using a combination boiler:
- You make savings on installation as there is less pipework needed
- There is no need for a hot water storage cylinder
- There is no need for the valves and fittings associated with a hot water cylinder
What Else Should I Know?
You should know that gas combination (Combi) boilers and system boilers are 'mains fed' operated systems, this means that the water is supplied to both the combi and system boiler at water mains pressure. This is called a 'direct' system.
Low pressure boilers used in hydronic central heating systems are 'gravity fed' meaning water is provided from a cold water storage cistern/tank sited at a high level. This is called an 'indirect' system.
Standard conventional gas boilers are being replaced with high efficiency boilers of both condensing and non-condensing types. Condensing combination boilers are now also available.
What is A Condensing Boiler?
A condensing boiler is a boiler that reuses the heat that would normally escape from the boiler flue to reheat water in a secondary heat exchanger. When hydrocarbon fuel such as coal, gas and oil are burnt, as part of the combustion process they combine with the oxygen in the air to form water vapour.
The latent heat that is used to produce this vapour forms a significant part of the heat given up by the fuel. Because this vapour leaves the boiler, together with the combustion gases through the flue, this heat is lost. If this vapour can be condensed into liquid within the boiler it can then give up this heat which can be transfered to the heating system therefore raising the efficiency of the process.
With boilers made from materials such as steel and cast iron it was important not to cool the combustion gases down to the 'dew point' which is about 55°C, the point where gas condenses to liquid. This liquid (condensate) is a corrosive acid that can attack boilers and flues.
Condensing boilers are made from stainless steel or cast aluminium/aluminum and therefore resistant to the mild corrosive acid of the condensate. The flue gases leave a condensing boiler at about 5 - 10°C above the return water temperature and this is cool enough to allow the use of plastic pipes for the flue construction.
Condensing boilers are also less harmful to the environment than conventional boilers because their high efficiency enables them to produce more heat from a given amount of fuel and because less harmful elements in the combustion gases are released into the atmosphere (even in non-condensing mode condensing boilers are still markedly more efficient than conventional boilers).
Types of Domestic Hydronic Central Heating Systems
There are a number hydronic central heating system choices at your disposal.
When the heat loss calculation have been made and the boiler sized the choices are as follows:
- Hydronic central heating boilers can be either conventional non-condensing, combination non-condensing, or both boilers types (conventional and combination) can be of the condensing type which is recommended because its more efficient and is environmentally cleaner than non-condensing boiler types.
- Fuel can be natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and oil. Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels are much higher for oil than natural gas and LPG. Solid fuel (wood, coal, wood pellets) boilers can also be used for hydronic central heating and domestic hot water (floor standing only).
- System-Link Hydronic Central Heating- automatic boiler (eg. conventional boiler) and solid fuel boiler linked both providing domestic hot water and space heating
Renewable energy systems:
- Thermal energy heating ground source heat pumps
- Air Source Heat Pumps
- Hydronic heating cooing water source heat pumps and
- Photovoltaic (solar panels)
Heat pumps can take low temperature from the soil, rock, water and air, and increase it to higher more useful temperatures suitable for underfloor heatingand/or hot water radiators.
Solar panels can provide the energy required to run the heat pump, making it a totally clean system.
- Mains pressure systems or low pressure system.
- Domestic hot water can be provided on demand by instantaneous/combination boilers, or from storage (hot water storage cylinder).
- Hot water storage cylinders can be either of the vented type (open low pressure systems) or the unvented type (mains pressure only)
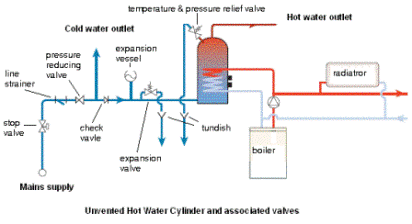
- Central heating systems can be either open to the atmosphere (vented) or sealed systems (not open to the atmosphere).
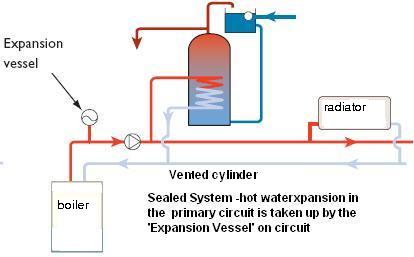
- Heat emitter selection - radiators, convectors or underfloor pipes.
- System management controls -
|
|
- multi channel programmers
- programmable room thermostats (both wired and Radio frequency)
- cylinder thermostat
- frost protection
- weather compensator (internal and external sensors)
- thermostatic radiator valves (TRV's) - TRV's do not reduce running costs and are really an unnecessary cost as the boiler is controlled by the room thermostat and not TRV's, although they are useful in large commercial and public buildings
- zone valves (motorized valves)
- automatic by-pass valve
- circulator pump
- automatic air vent and boiler interlock (boiler interlock is a wiring arrangement to ensure that the boiler only fires on demand for hot water or heating, and not from its own internal thermostat)
- a system boiler incorporates an automatic by-pass valve, circulator pump, diverter valve, expansion vessel and automatic air vent - designed to simplify and speed up installations.
- Backflow protection - Air-gaps, check valves and zone valves prevents water contamination due to back-siphonage and secondary circulation.
- Pipe material selection - copper or plastic, the most common plastics are Polybutylene (PB), Crossed Linked Polyethylene (PEX) includes a barrier pipe which incorporates an oxygen barrier, and Multi-Layer Composite pipes (MLC) that also include the oxygen barrier.
There are a number of factors governing a good heating system, however the efficiency of any home heating system is dependent on good home insulation.
See also:
- DIY Heating Plumbing Tips 5
Central Heating Systems Problems - Central Heating Design
- Two Pipe System
- Underfloor Heating
- Hot Water Radiators
- Radiant Heat
- Hydronic Heating System Expansion Tank
- Cold Water Systems
- DIY Heating Plumbing Tips 3
Residential Heating And Hot Water Controls - Hot Water Baseboard Heating Systems
Click here to visit online store.
Home Heat Loss Heat Gain Radiant Heat Central Heating Radiators UFH
Heat Pumps GSHP's WSHP's ASHP's Solar Heating PV Systems Boilers
Water Heaters Insulation Elec-Heaters
Terms of Use | Privacy | Contact Us

|
Visitors Say
Hi, My name is Shannon and I'm one of home-heating-systems-and-solutions.com readers. I'd like to thank you for the excellent information I've found on home-heating-systems-and-solutions.com, it's one of my favorite readings on the net. Warmest Regards Shannon United States
Thanks for the advice for removing an air lock from an indirect system. Had to change an inlet on my cistern. First time I have tried any home plumbing. After draining the cold tank system air locked when I refilled the tank. Garden hose and mains pressure up the tap sorted my problems. Would not have known what to do without the advice on the site. Many thanks Sean United Kingdom.
An excellent site. I have found it very usefull. I am currently in the design phase of a new house and have be pondering which heat system to use. From your site I have been able to choose the right system. Ross New Zealand
I enjoyed your site. Pat United States
We're so excited to announce our first Children Book
The Special and Talented Dog Show
To order click here
The second book published is called
Flying Things
This is aimed at a pre-school audience and is a rhyming story. You can buy by clicking here
To read more about our children's books, click here